Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification is an internationally recognized, third-party green building certification system. The LEED certification program operates under the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) and focuses on recognizing eco-friendly design and construction decisions.
Benefits of Becoming LEED-Certified
Along with the environmental benefits of becoming LEED-certified, there are commercial advantages, including tax rebates, lower insurance premiums, and zoning allowances. The incentives of becoming LEED-certified have helped stimulate more than 500,000 LEED-certified housing units globally, with more than 400,000 located in the United States.
Incentives
The incentives for green building can be divided into two main categories: structural incentives and financial incentives. Financial incentives can be seen in the form of tax credits, fee reductions or waivers, grants, and revolving loan funds. Structural incentives include expedited permitting processes and density bonuses. In certain municipalities, additional incentives can come in the form of certification planning or marketing assistance.
Saving Money
Becoming LEED-certified seems like a heavy upfront investment, but a massive amount of savings on utilities can be seen in the first month after having received certification. LEED-certified buildings use up to 20%–30% less energy than comparable buildings built to code, according to the USGBC.
Health Benefits
LEED-certified buildings have a number of criteria to meet regarding health and well-being. From the beginning of the building process, LEED-certified buildings use nontoxic chemicals and green construction material. Additionally, the air quality of LEED-certified buildings is higher due to minimized exposure to toxins and pollutants. LEED-certified buildings also install dehumidification systems that control the moisture level indoors, which helps provide comfort, increase long-term durability, and reduce the risk of mold or mildew.
LEED-certified buildings are also built close to public transportation, helping to reduce the carbon footprint of car commutes and encourage occupants to use public transportation.
Reduced Ecological Footprint
LEED-certified buildings are committed to reducing buildings’ climate impact from the start of the construction process. The design process of LEED-certified buildings takes into account the energy, water consumption, and materials used to help reduce the building’s ecological footprint.
How to Become LEED-Certified
Earning a LEED certification is a rigorous process involving thorough testing of every aspect of the building. There are multiple levels to achieve before becoming fully certified. Following is a breakdown of the rating system and levels required to become LEED-certified.
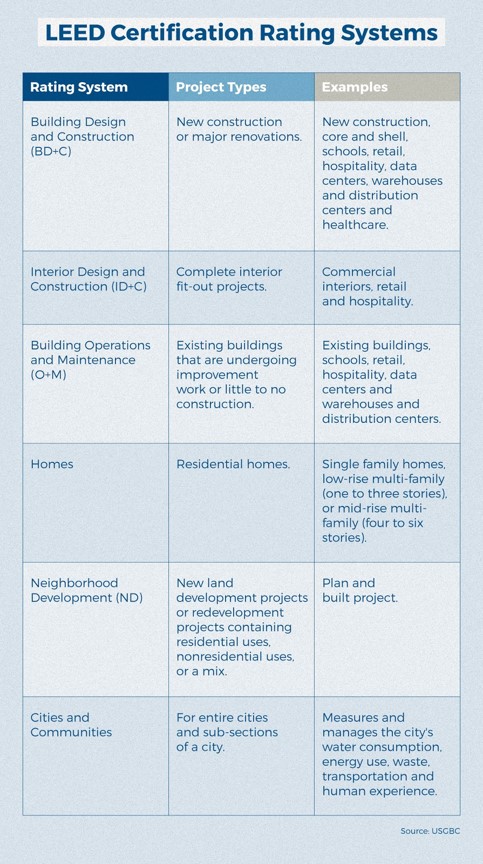
There are five rating systems, broken down by building type, including building design and construction, interior design and construction, operations and maintenance, homes, neighborhood development, and cities and communities.
LEED certification has four primary levels, which are attained by the number of total points earned at the end of the certification process. Points can be earned for each sustainable design element added to a commercial building. The certification levels are:
Hiring a LEED-Certified Professional
Becoming LEED-certified isn’t easy, especially when trying to achieve a specific level of certification. Hiring a LEED-certified consultant to help you with the process is recommended. LEED Accredited Professionals (APs) are consultants who are educated on the most recent strategies of green building design and construction to help you achieve the certification level you desire.
The Bank of America building in New York is LEED-Certified Platinum, the highest certification level available.
Future of LEED Certification
Sustainable construction is a rising trend in the construction industry, but many buildings are slow in adapting to these new methods of environmentally friendly design. High energy consumption is an undeniable issue that is impacting us all.
Fatih Birol, PhD, the executive director of the International Energy Agency, says, “If we don’t make buildings more efficient, their rising energy use will impact us all, whether it be through access to affordable energy services, poor air quality or higher energy bills.”
To make a real change, we need a shift in attitude toward sustainable living. LEED certification is helping lead the charge toward sustainable construction, with 21.2% of the U.S. commercial office design market now opting for green buildings. It’s becoming clear green building is the future of the construction industry.
Interested in becoming LEED-certified? For a step-by-step guide on achieving LEED certification, check out FurnaceCompare’s in-depth article on everything you need to know about LEED certification.
Steps to Achieve LEED Certification
Although achieving LEED certification can be lengthy and laborious, there are nine primary steps to complete.
- Meeting minimum requirements. To achieve the minimum requirements, you must be in a permanent location on existing land, use reasonable LEED boundaries, and comply with project site requirements.
- Identify rating system. For new commercial buildings, refer to the LEED v4 for Building Design and Construction.
- Register project. Register your project online using the LEED online portal, where you will complete registration information, submit payment, and sign the certification agreement.
- Select your project team. This includes the project owner, an agent, a builder, an architect, an engineer, and any other necessary members.
- Verify your project. To ensure your project stays on track, facilitate on-site verifications during your design and construction process.
- Pay certification fees. Once done submitting documentation, you must pay the appropriate certification fees. These fees can vary greatly based on building specs and usually range from $2,250 to $22,500, depending on project size.
- Begin the review process. This includes a preliminary review, final review, and potential appeal review.
Achieve project certification. The final step is to either accept or repeal the Green Building Certification Inc.’s final certification. Based on the number of points you achieve, you will be certified on one of the four levels mentioned above.
| Drew Page is a writer from San Diego, California. He loves learning, writing and playing music. When not surfing the web, you can find him actually surfing, in the kitchen or in a book. |


