Despite a slow start to the hurricane season, “the next Ida or Sandy could still be lying in wait,” warned FEMA Administrator Deanne Criswell.
Atmospheric and oceanic conditions still favor an above-normal 2022 Atlantic hurricane season, according to NOAA’s annual mid-season update recently issued by the Climate Prediction Center, a division of the National Weather Service.

“I urge everyone to remain vigilant as we enter the peak months of hurricane season,” said Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo. “The experts at NOAA will continue to provide the science, data, and services needed to help communities become hurricane resilient and climate-ready for the remainder of hurricane season and beyond.”
NOAA forecasters have slightly decreased the likelihood of an above-normal Atlantic hurricane season to 60% (lowered from the outlook issued in May, which predicted a 65% chance). The likelihood of near-normal activity has risen to 30%, and the chances remain at 10% for a below-normal season.
“We’re just getting into the peak months of August through October for hurricane development, and we anticipate that more storms are on the way,” said NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad, Ph.D. “NOAA stands ready to deliver timely and accurate forecasts and warnings to help communities prepare in advance of approaching storms.”
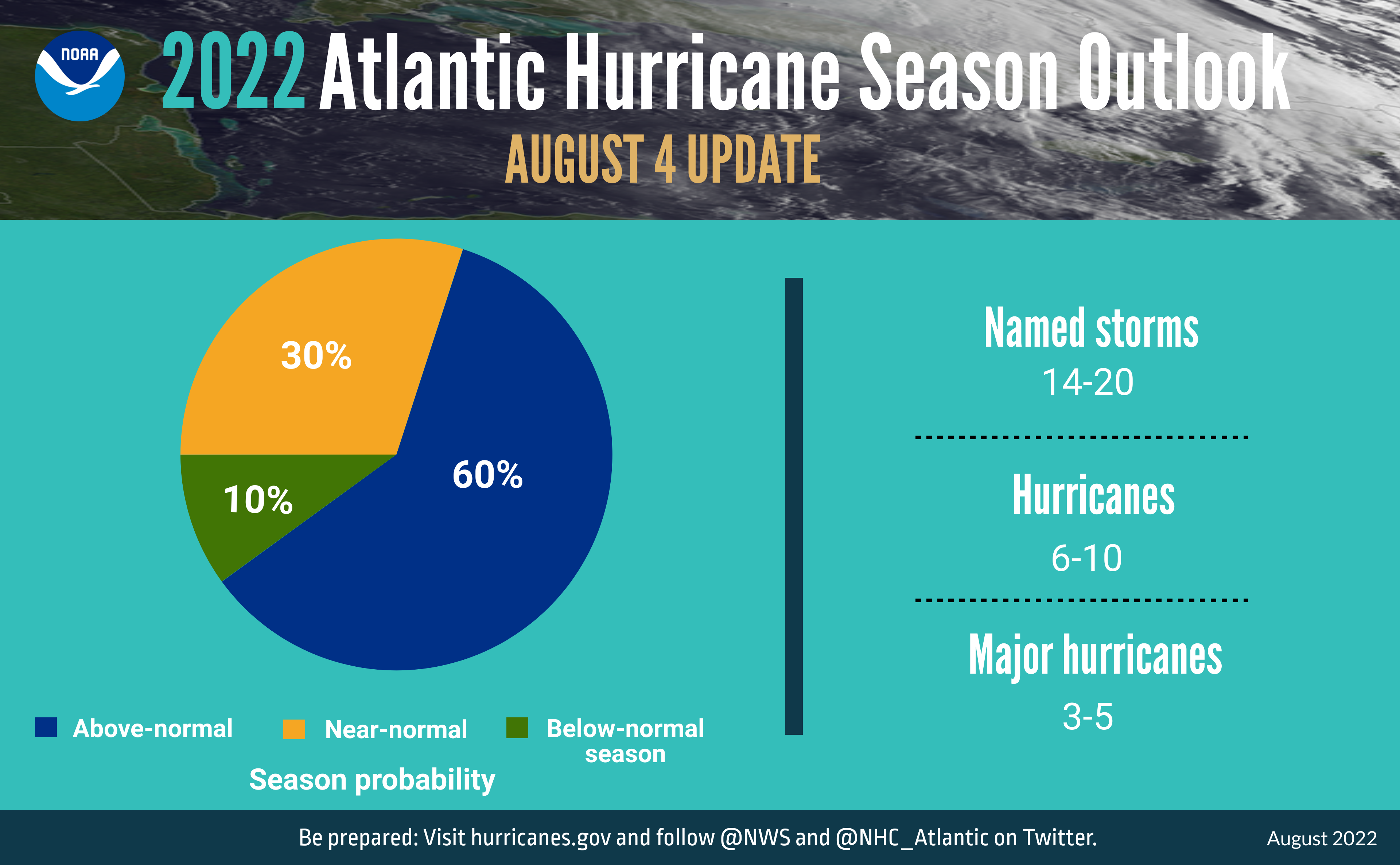
NOAA’s update to the 2022 outlook—which covers the entire six-month hurricane season that ends on Nov. 30—calls for 14-20 named storms (winds of 39 mph or greater), of which 6-10 could become hurricanes (winds of 74 mph or greater). Of those, 3-5 could become major hurricanes (winds of 111 mph or greater). NOAA provides these ranges with a 70% confidence.
So far, the season has seen three named storms and no hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin. An average hurricane season produces 14 named storms, of which seven become hurricanes, including three major hurricanes.
ALSO READ: Back to Basics: Preparing Your Facility for Hurricanes
This outlook is for overall seasonal activity, and is not a landfall forecast. Landfalls are largely governed by short-term weather patterns that are currently only predictable within about one week of a storm potentially reaching a coastline.
There are several atmospheric and oceanic conditions that still favor an active hurricane season. This includes La Niña conditions, which are favored to remain in place for the rest of 2022 and could allow the ongoing high-activity era conditions to dominate, or slightly enhance hurricane activity. In addition to a continued La Niña, weaker tropical Atlantic trade winds, an active west African Monsoon, and likely above-normal Atlantic sea-surface temperatures set the stage for an active hurricane season and are reflective of the ongoing high-activity era for Atlantic hurricanes.

“Communities and families should prepare now for the remainder of what is still expected to be an active hurricane season,” said Ken Graham, director of the National Weather Service. “Ensure that you are ready to take action if a hurricane threatens your area by developing an evacuation plan and gathering hurricane supplies now, before a storm is bearing down on your community.”
Learn about NOAA’s hurricane science and forecasting expertise by viewing our Hurricane Season Media Resource Guide and stay tuned to the National Hurricane Center for the latest about tropical storm and hurricane activity in the Atlantic.
“Although it has been a relatively slow start to hurricane season, with no major storms developing in the Atlantic, this is not unusual and we therefore cannot afford to let our guard down,” said FEMA’s Criswell. “This is especially important as we enter peak hurricane season—the next Ida or Sandy could still be lying in wait. That’s why everyone should take proactive steps to get ready by downloading the FEMA app and visiting Ready.gov or Listo.gov for preparedness tips. And most importantly, make sure you understand your local risk and follow directions from your state and local officials.”
