As facilities management professionals, you can never be too prepared for power outages or emergencies. Facilities need to maintain operations and prevent potential losses that can result from power outages.
When an unexpected storm, wildfire, or other natural disasters happen, facilities depend on uninterrupted backup power. But when a generator sits for too long without any maintenance, it can fail when you need it working the most.

Planned maintenance for your generator ensures it will not cause failure during power outages and emergency situations. In addition, regular maintenance minimizes the risk of mechanical failure and identifies potential issues before they worsen.
What should be done to maintain the longevity of your generator? There are certain tasks facilities managers can perform themselves, while other maintenance tasks are complex and require a professional.
Routine Maintenance for Your Generator
Following a maintenance schedule for your backup generator involves several ongoing tasks that support your generator’s critical systems. Regular maintenance tasks will help identify potential issues that could hinder it from properly functioning while prolonging the lifespan of the generator. Here is a list of ongoing maintenance tasks for your backup generator:
1. Regular Oil and Oil Filter Changes
Oil and oil filter changes help keep your generator’s engine running smoothly. Check the oil levels regularly to make sure they are full with the correct oil type and grade, as recommended by the manufacturer. In addition, inspect the oil filter and replace it as needed.
Generally, an oil and filter change should occur after 500 hours of use or yearly for standby generators not in use.
2. Fuel Level and Quality
For long-term preventative maintenance of your generator, use clean, high-quality fuel. If you use gasoline, ensure it is fresh and not contaminated. For diesel generators, consider adding a fuel stabilizer to prevent microbial growth and maintain fuel quality.
Check your fuel level regularly, and keep it sufficiently filled. If your backup generator is not used for extended periods of time, consider either draining the fuel or using a fuel stabilizer to prevent deterioration.
3. Air Filter Replacement
Generally, an air filter inspection and replacement should occur every six months. However, a few factors can affect how often you replace air filters. The placement of your generator and surrounding environment can affect the need for replacement more often.
4. The Cooling System
A properly maintained cooling system keeps your generator from overheating, which could severely damage the generator. Monthly cooling system inspections will maintain coolant quality and extend the life of your standby generator.
Regularly inspecting your cooling system includes inspection of the radiator and coolant levels, as well as looking for any signs of leakage, blockage, and general wear-and-tear. In addition, clean any build-up of debris or dirt from the cooling fans and make sure the system is functioning correctly.
5. Battery Care
If your backup generator has a battery, ensure the battery is charged. If your generator battery is not well-maintained, it can lead to generator failure during emergencies when your facility most needs backup power.
Check the battery connections for corrosion or looseness, which can prevent the flow of electrical current. Make sure the terminals and connections are clean and free of dust or dirt. Generally, your generator’s battery should be changed every 2-5 years. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for additional battery replacement and maintenance for your generator.
6. Regular Visual Inspection of a Generator’s Electrical Connections
A visual inspection is the first line of defense in keeping your electrical system up and running. Any faulting electrical components could result in failure to engage and even fire.
Make sure the generator is turned off and disconnected from the power source before proceeding with your inspection. Tighten loosened connections and clean or replace corroded connections.
Generator Preventative Maintenance Checklist
Following a maintenance schedule helps prolong the life of your backup power generator and ensures it is ready to provide power immediately during emergencies.
Here is a checklist for weekly, monthly, bi-annually, and yearly generator maintenance.
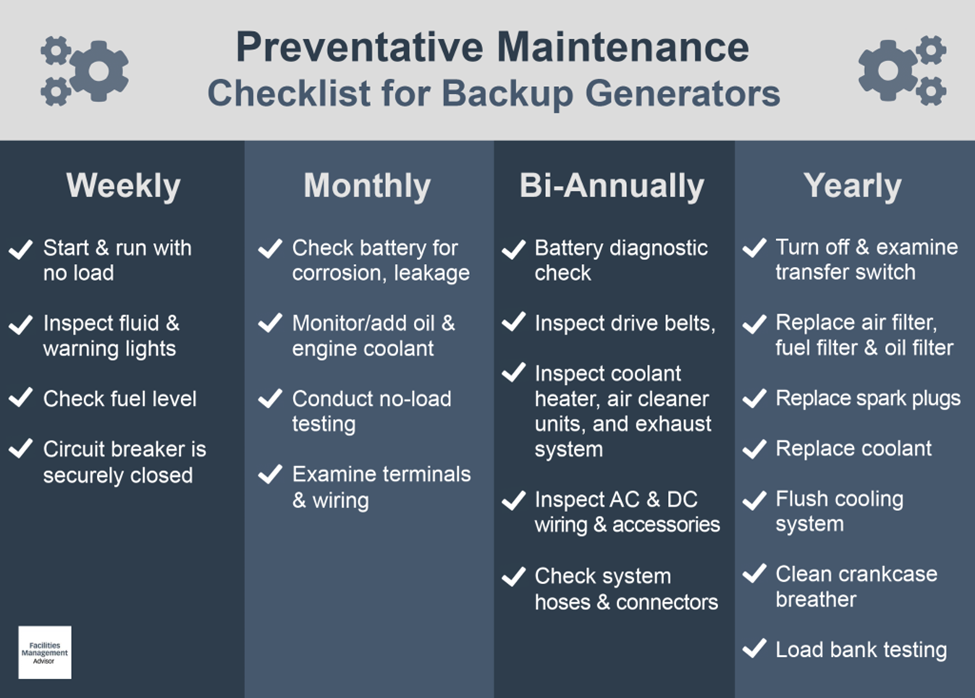
Weekly Maintenance:
- Start and run your back generator with no load.
- Inspect for fluid leaks and warning lights around the unit.
- Check the fuel level, and confirm the fuel tank is full, with the appropriate fuel used.
- Ensure the circuit breaker is securely closed.
Monthly Maintenance:
- Check the battery for proper charges and signs of corrosion or leakage.
- Monitor oil and engine coolant levels, and add oil and coolant as necessary.
- Conduct no-load testing to provide your generator with regular exercise.
- Examine unit terminals and wiring for loose wires, clamps, and potential corrosion.
Biannual Maintenance:
- Perform an in-depth battery diagnostic check.
- Inspect drive belts.
- Inspect the exhaust system.
- Inspect air cleaner units.
- Inspect the coolant heater.
- Check coolant lines and connections.
- Inspect AC wiring and accessories for signs of damage or loose connections.
- Inspect DC wiring system and accessories (including a check to see if your control panel is functioning correctly).
- Check all system hoses and connectors.
- Inspect for fuel and oil leaks.
Annual Maintenance:
- Carry out load bank testing.
- Turn off and examine your transfer switch.
- Replace the air filter, fuel filter, oil, oil filter, spark plugs, and coolant.
- Flush the cooling system and verify the correct coolant concentration.
- Clean the crankcase breather.
Record-Keeping for Generators
Record-keeping is important for tracking the history of your generator’s maintenance. Create detailed maintenance logs that include date, maintenance task, and names of technicians involved.
Not only do records verify maintenance completion and information for warranty and insurance, but they also provide facilities management professionals with peace of mind.
Another reason record-keeping is important is it helps regarding reselling your backup generator. Potential buyers will require detailed and up-to-date maintenance records of your generator to assess resale value.
How Long Should a Backup Power Generator Last?
Proper maintenance can improve the life expectancy of your backup generator. By planning out scheduled maintenance and following the checklist above, facilities management professionals can greatly reduce unexpected breakdowns and maintain optimal condition and performance.
A new backup generator should last about 20 to 30 years, and should be reliable for 10,000-30,000 running hours. However, the level of maintenance of your generator, along with other factors like frequency of usage and environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), can determine longevity and when you will need a new generator.
Closing Out: Scheduled Maintenance for Generator Longevity
A backup generator is a valuable investment for any facility. To get the most out of your investment, maintenance is essential to prolonging your generator’s lifespan, ensuring it functions during power outages or emergencies. Use this checklist as a starting point, and always let a professional service the system for major repairs.
Dick Davis is president of Depco Power Systems. The company is a supplier of power generation equipment worldwide, providing new and used generators, generator sets, engines, marine transmissions, power switches, and diesel engine parts.
